Access your own patient portal, provided by NCSH.
Orthopedics
What is MAKO Robotic Surgery?
Fri, Aug 12, 2022

Joint replacements, especially involving knees, are some of the most common and safest surgical procedures performed. Robotic assistance makes them even safer for patients. MAKOplasty is surgery performed with the MAKO robotic arm. Surgeons use it to plan and implement minimally invasive knee and hip replacement surgeries.
About Robotic Surgeries
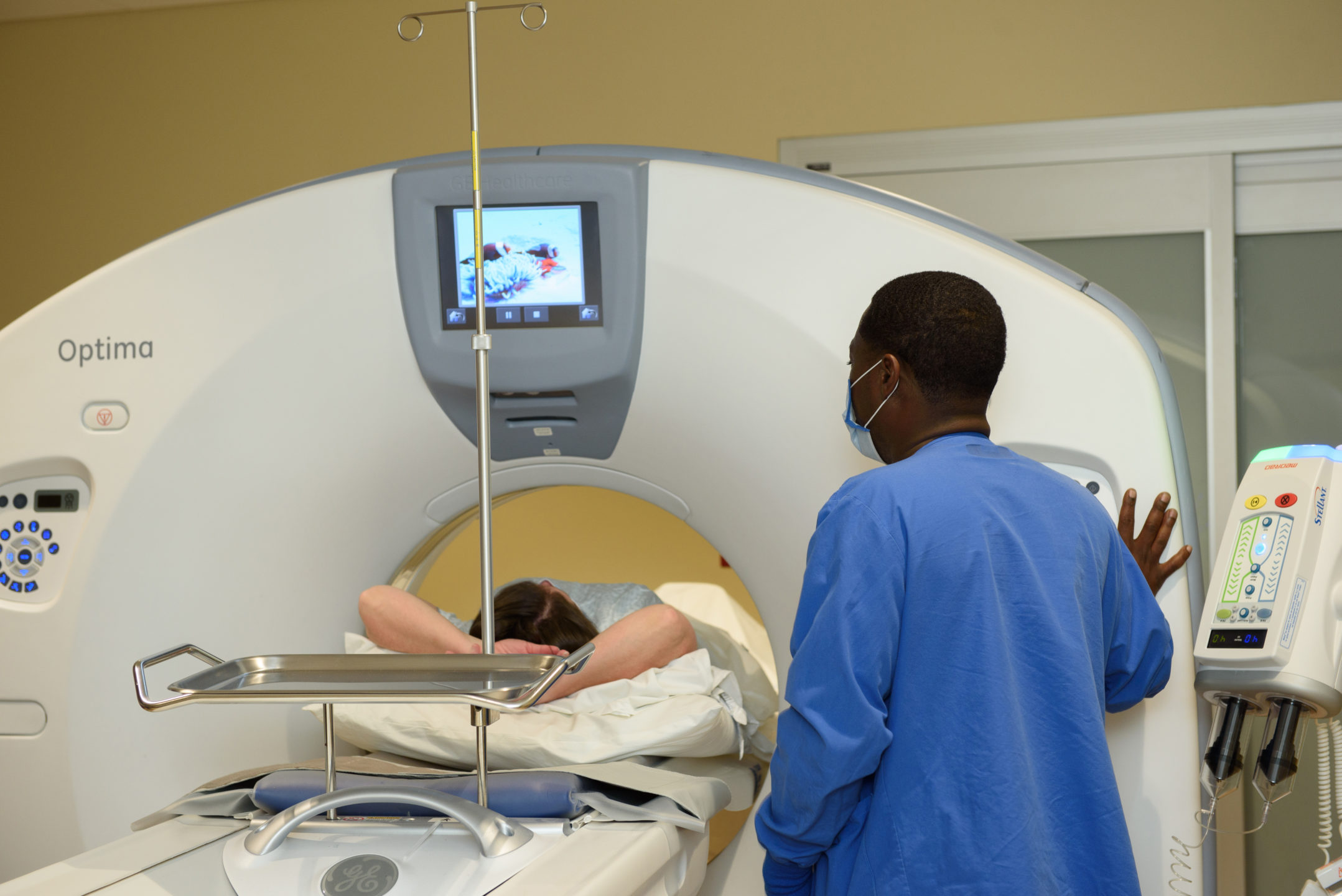
Robotic surgery, or, more accurately, robotic-assisted surgery, is a procedure involving a surgeon controlling a robotic arm. The arm performs the operation using small incisions and tools, while the surgeon controls it through a computer.
The first robotic procedures occurred in the 1980s—including the first robotic total knee arthroplasty performed in the United Kingdom in 1988—and they have evolved considerably since then. There are many reasons surgeons use a robotic arm:
- A robotic system helps a surgeon plan and execute a procedure more accurately.
- It allows them greater control over the positioning of the artificial joint.
- Robotic assistance in joint replacement requires only very small incisions, which improves patient outcomes, pain, and recovery times.
- Implanted joints last longer when inserted with robotic assistance, likely due to better alignment of the components.
Patients often prefer robotic-assisted surgery for all of the same reasons. It leaves less room for error; allows for minimally invasive, accurate procedures; and generally results in better outcomes and quicker recovery times.
What is MAKO Robotic Arm-Assisted Surgery?
MAKOplasty is surgery conducted with MAKO robotic systems. The MAKO systems are made by Stryker, a medical technology company, and are used to assist in all kinds of orthopedic surgeries. These include joint replacement, foot and ankle surgery, spine surgery, trauma treatment, and more.
MAKO Hip and Knee Replacement Surgeries
Whether used for a knee or hip replacement procedure, the MAKO robotic surgery system begins with an individualized treatment plan. Following a CT scan of the joint, the surgeon uses a 3D model of it to plan the details. These include the selection and size of the artificial component and how they will place and position it in the joint space.
In the first part of the surgery, the surgeon uses the robotic arm to remove damaged tissue, such as bone and cartilage that has deteriorated due to arthritis. Once they have removed the diseased tissue, the surgeon can use the robotic arm to place and situate the artificial joint.
During the procedure, the MAKO arm sends data to the surgeon. This allows the physician to assess the progress of the surgery and make adjustments as needed. It also ensures that the surgeon stays within a boundary defined by the surgical plan.
What Are the Benefits of MAKO Surgery?
According to a study of MAKOplasty software, the system produces accurate and reproducible measurements used in preparation for a total knee replacement. This is an essential preparatory part of joint replacement that ensures the procedure goes smoothly and the implant is positioned correctly.
There are many benefits of MAKO-assisted joint replacements, according to Stryker and studies:
- The robotic procedure preserves more healthy bone tissue, which is better for overall joint health and functioning.
- Studies of knee arthroplasty also show that the system better protects healthy soft tissue from damage.
- Studies of artificial hips show that using this system reduces the risk that the new joint will become dislocated.
- There is less loss of blood during surgery with a robotic procedure.
- Patients report the feeling of a new hip is more natural.
- Reports indicate that patients undergoing a MAKO procedure had less pain six months later than those who had traditional joint replacement surgery.
- Those patients also reported higher overall satisfaction with the procedure and its outcomes.
North Carolina Specialty Hospital is pleased to offer patients the option of robotic surgery using the MAKO system. To learn more about it and find out if you are a good candidate for hip or knee replacement, contact us to request an appointment with an orthopedic joint specialist.
RELATED NEWS
Kyphoplasty: Understanding Your Options for Spinal Compression and Fractures
Back and spine pain can be very limiting. Compression fractures in the spine are common sources of pain with several treatment options. A procedure called kyphoplasty can help restore spinal stability and relieve pain. Learn…
Continue Reading

What Are 2 Warning Signs of a Rotator Cuff Tear?
Do you have sharp pain or weakness in your shoulder? They could be warning signs of a rotator cuff tear. NCSH explains what you must know and do.
Continue Reading
Stay Current
Educational Articles & More
View News & Press
